Categories Products for Mass Spectrometry In-vivo Mouse SILAM Proteomics/Metabolomics
In-vivo Mouse SILAM Proteomics/Metabolomics
Stable isotopic labelling is the most reliable and accurate method for quantitative proteomics and metabolomics. Proteomics studies on uniformly 15N-labelled rats have been previously reported using 15N-labelled algae as protein source for Stable Isotope Metabolic Labelling in Mammals (SILAM).[1]
Silantes provides
- SILAM Mouse Diets (diets vor other model organisms such as fly and worm are available on request),
- SILAM Mouse Tissues wet and
- SILAM Mouse Tissues lyophilized on request.
- New: 13C-SILAM Mouse diets are now available!
Silantes 15N-SILAM Diets for in-vivo labelling of mice
Silantes has developed a 15N-diet in cooperation with the group of Professor Chris Turck, Max-Planck-Institute of Psychiatry as a kit containing a 15N-labelled “heavy” diet (B) and unlabelled “light” diet (A).[2] It is an artificial feed using Harlan components and a hydrolysate of the bacteria Ralstonia eutropha as 15N-protein source. Feeding experiments showed that the mice accepted bacterial-based protein better than algae-based protein.
After the metabolic labelling (feeding) of the mice according to the scheme in figure 2 or figure 3, the mice are sacrificed. Differences in the protein patterns are determined in analogy to the established SILAC approach in cell culture (see literature for Silantes in vitro SILAC).
A variation of the in-vivo SILAM-approach is the “spike-in” approach.
SILAM spike-in using Silantes 15N-labelled mouse tissue
Figure 2 shows the SILAM spike-in workflow: Differences in protein patterns of unlabelled case tissue with respect to unlabelled control tissue can be quantified by “spiking-in” a 15N-labelled reference tissue.
This 15N reference tissue can be obtained from Silantes directly, as frozen material or lyophilized.
Short outline of the procedure:
The isotopically labelled “heavy” reference tissue is mixed with the unlabelled “light” case and control tissue, respectively. The proteomes of the case/reference-mix and control/reference-mix are isolated, digested and subjected to LC-MS. Therefore, the two peptide amount ratios can be determined in analogy to the in-vivo SILAC-workflow to determine the case/control ratio (see Silantes in-vivo SILAC literature).
In addition to spiking-in the 15N-tissue as reference material for relative protein quantification by mass spectrometry, the SILAM approach is used in further applications such as
- Partially labelled mouse specimens for global protein turnover analysis by mass spectrometry (see figure 2)[3]
- Labelled metabolite standards for molecular structure confirmation
- Biomarker discovery and verification
Silantes 13C-SILAM Diets for in-vivo labelling of mice
If the goal is to detect and relatively quantify a large number of metabolites in an untargeted manner, lower organisms can be fed or mammalian cells grown with a diet or media, respectively where 12C is replaced with the stable 13C isotope. The generated tissue or cellular material can then be used as isotope-labelled internal standard reference. This approach has been successfully established for microorganisms and was subsequently extended to plants and small animals.
Silantes has developed a diet to 13C-label mice with the aim of producing isotope-labelled material as reference for metabolomics studies.
Preliminary studies by us have shown that the partially 13C-labelled mouse reference material can be used for the relative quantification of amino acids in human plasma samples. We envision that this approach can be extended to the relative quantification of other small molecules of interest in metabolomics research.
We have developed 2 diets for metabolic 13C-labelling of mice:
- Partially 13C-labelled SILAM mouse diet based on Ralstonia eutropha biomass with a 13C isotopic enrichment of > 20 atom %.
- Uniformly 13C-labelled SILAM mouse diet based on Arthrospira maxima ("Spirulina") biomass with a 13C isotopic enrichment of > 98 atom %.
Metabolomics Study using the Partially 13C-labelled SILAM Mouse Diet
We have shown that amino acids in human plasma samples can be relatively quantified using reference material from mice fed for 14 days with the partially 13C-labelled diet.
Mouse amino acids from tissue and blood had up to 75% 13C enrichment levels
although the initial diet only had a 13C enrichment of ~20%.
Figure 1 shows the 13C enrichment of free amino acids in mouse plasma, heart tissue and plasma protein hydrolysates mapped on a simplified metabolic pathway. The overall average 13C enrichment was ~ 65%. Essential amino acids showed particularly high 13C isotope enrichment. This is due to the fact that essential amino acids cannot be produced by the organism itself and proteins from the partially 13C-enriched feed serve as the main protein source.
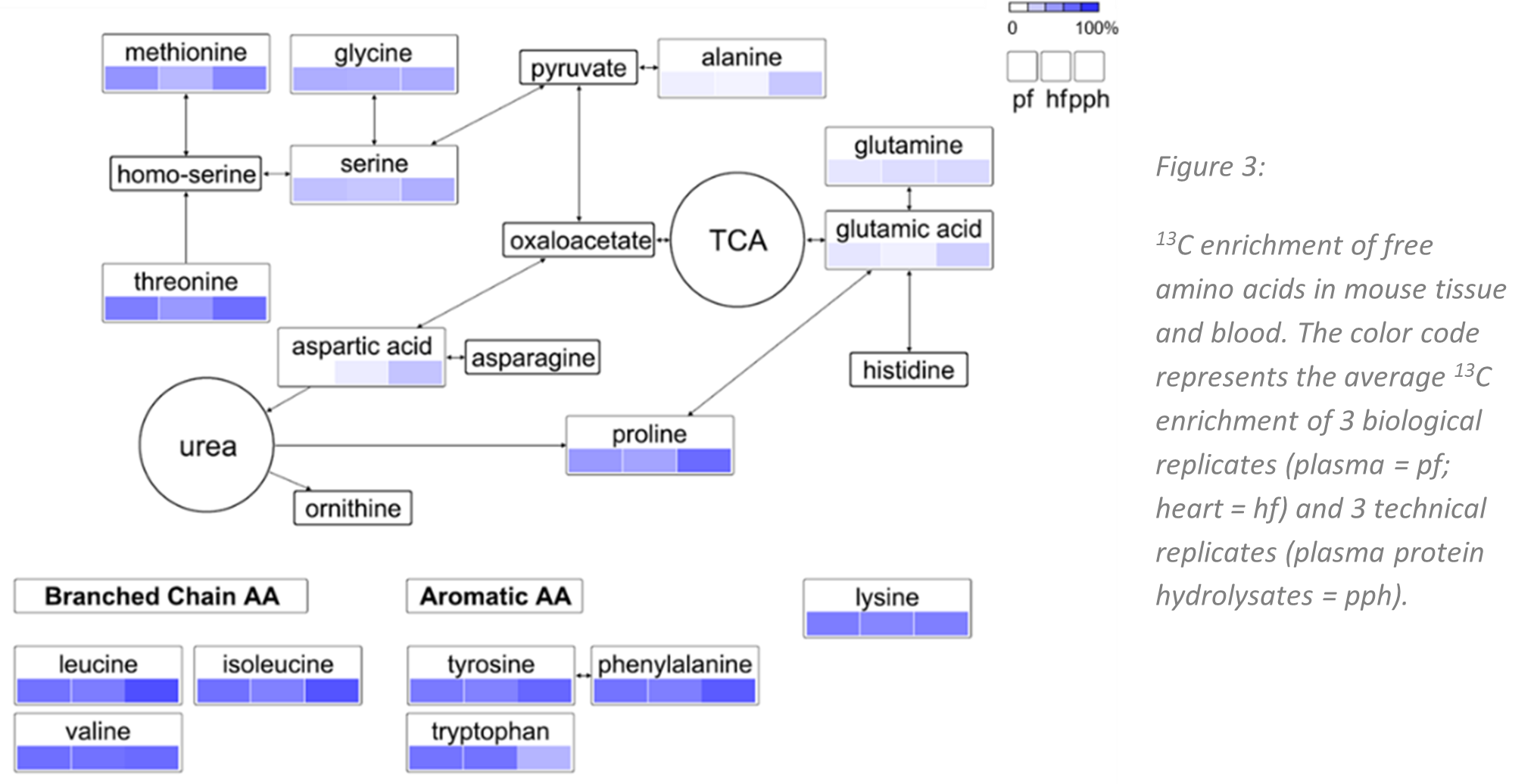
For the relative quantification of amino acids in human plasma samples, the partially 13C-labelled mouse reference material turned out to be a very valuable source. Since mice share many metabolic pathways with humans it is conceivable that our approach can be further extended to other small molecules of interest in human metabolomics research.
In addition, mouse 13C-labelled blood and tissue material can serve as valuable reference for metabolomics studies of mouse models, to verify biomarker candidates and aid in their identification
[1] Daniel B. McClatchy, Meng-Qiu Dong, Christine C. Wu, John D. Venable and John R. Yates (2007) 15N Metabolic Labelling of Mammalian Tissue with Slow Protein, Journal of Proteome Research, 6(5), 2005-2010.
[2] Zhang, M.D. Filiou, G. Chen, H. Heumann, Chris W. Turck (2008). Biomarker discovery in a mouse model of trait anxiety using 15N metabolic labeling, Poster HUPO Amsterdam.
[3] Zhang, Reckow S, Webhofer C, Boehme M, Gormanns P, Egge-Jacobsen WM, Turck CW. (2011) Proteome scale turnover analysis in live animals using stable isotope metabolic labeling. Anal Chem 83:1665-1672.
|
|
SILAM Mouse Tissue wet
|


